Page Contents
Minute paper: How to not disturb flows with dye?
Take a few minutes to think for yourself before reading these answers from class:[/vc_column_text]
- Match fluid properties, including
-
- velocity(speed and direction)
- vorticity
- density
- viscosity
- polarity; miscibility (will it mix)
- pressure
- temperature
- molecular weight
- intermolecular forces (to minimize surface tension effects)
- diffusion coefficient
- Ensure there is no undesirable chemical reaction between the dye and ambient fluid
- Inject upstream of test section or region of interest (ROI)
- Use small ports
- Minimize volume injected
- Premix a dilute solution of dye with the ambient fluid to help match properties.
Very importantly, consider the location where the dye is injected; a slight change in location can reveal very different physics, as demonstrated in Figure 1. This is a still from a six minute film collecting the work of Henri Werlé, a master of colored dye streams. It’s a beautiful little film, with a cool 1970’s soundtrack.
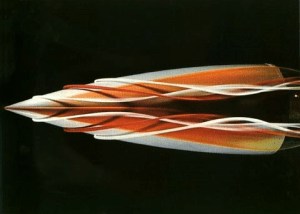
In the 1970s Werlé worked at ONERA, the NASA of France, and built a large vertical water tunnel for these experiments. I’d love to find a biography of him!
If you are interested in flow over an object, a slick method for marking the flow that passes over the surface is to coat the surface with a water-soluble paint like tempera, and let it dry before submerging it in the flow. By marking the flow that actually touches the surface you are marking the fluid in the boundary layer that acquires vorticity and is shed into the wake. You could also coat short strings on a rake to make weak streamlines visible. This will probably work for low-speed flow with short run times, but I haven’t seen good examples.

A similar idea is to freeze dyed water, then place the colored ice cube in water. The dye then marks where the melt water goes, as shown in Figure 2.This technique is used on a giant scale to study where the flow from melting glaciers goes.
Many of the suggestions above involve matching the properties of the marked/dyed/seeded flow and the transparent ambient fluid. It’s tough to match all these properties! A big reason is that dye properties are different from ambient fluid. Food coloring, in particular, is made of a water and propylene glycol base which is slightly more dense than water, with the dye dissolved in it. As mentioned above, dyes are generally large molecules, with correspondingly large molecular weights. The result is that most food coloring will sink in water and in milk. If you want a neutrally buoyant dye, try a premix: the dense food coloring plus some isopropyl (rubbing) alcohol which floats.
Diffusion coefficients tell you how fast one type of molecule will spread itself through another type via diffusion, i.e. by Brownian motion, just the random motion of molecules bouncing around. Molecules always diffuse from where their concentration is high into where it is lower. For example, let’s say you’ve marked some water with dye, and dropped the dyed mixture into pure water. If the diffusion coefficient of the dye in water is higher than the self-diffusion coefficient of water, the dye will diffuse out of the droplet and into the ambient liquid, even though the water of the original droplet stays where it is. So the droplet will appear to spread, even though only the dye has moved. But if the diffusion coefficient of the dye matches that of the water, they will diffuse at the same rate, and the dye will truthfully continue to mark the location of the droplet fluid. In reality, the dye coefficient of blue dye in water is about 1/3 of water in water, so the water will diffuse out of the droplet faster, and the dye will lag behind. In any case, diffusion is a slow process compared to most of the fluid motions we are interested in, so we don’t need to worry . But if you are studying the details of mixing, down to a molecular level, do pay attention!
Turbulence also causes fast mixing, making visualization of the overall flow structure difficult. Dyes mix so rapidly that it will just look like a fog. If you can’t slow the flow back down into the laminar regime, try using something like milk or latex paint to carry your dye. It will hang together better, but it won’t capture the fine details of the mixing process.
Famous example of boundary marking technique:
Before computer generated imaging (CGI) it was difficult to simulate clouds in movies. The cloud tank was invented by Douglas Trumbull to make realistic clouds for Close Encounters of the Third Kind, a 1977 science fiction film written and directed by Steven Spielberg . The aliens’ ships arrive in Earth’s sky masked in quickly growing cumulus type clouds, as seen in this illegal clip :

“The effect’s process begins with filling a water tank halfway with saltwater which is then layered with a thin plastic sheet. Fresh water is poured over the thin layer of plastic to fill the rest of the tank. This leaves the visual effects artist to remove the thin layer of plastic to reveal what seems to be a single body of water, but is really two layers of different densities: salt water and fresh water. Finally, paint is injected into the tank and it flows through the water, forming an organic cloud figure… A 2000 gallon glass tank was used that was approximately seven feet tall, seven feet wide and four feet deep which would have to be emptied and refilled after every shot.”
Cloud tanks were used in a number of fantasy and science fiction films for the next 20 years, including Raiders of the Lost Ark (1981), Star Trek: The Wrath of Khan (1982), Ghostbusters (1984) and Independence Day (1996) [. There are a number of YouTube videos from people exploring this technique on a small scale: . You’ll notice that it’s hard to maintain good focus on the clouds when viewed from the side, perhaps because salt and fresh water have different indices of refraction and the clouds are right at the interface. I would recommend using a great deal of light so that you can use a small aperture for the best DOF, or viewing up through the bottom of the tank if possible.

